Theme:
MICROBIOLOGY CONF 2023
Conference series welcome all the participants globally to the upcoming conference “4th International Conference on Molecular Microbiology” scheduled on August 17-18, 2023 which will take place in Dublin, Ireland. This conference mainly focuses on the theme “Evolution and Exploration of Molecular Microbiology”.
Microbiology Conf 2023 provides you with a unique opportunity to meet up with peers from both academic circle and industries level belonging to Microbiology and have been designed in an interdisciplinary manner with a multitude of tracks to choose from every segment and it explore creative technologies regarding Drug discovery Technologies in Antibiotics and Microbial Biofilms at the universal scale and aims to accomplish the targeted scientific sessions and recent advancements in the field of Molecular Microbiology. The goal of this conference is to deliver an outstanding program for exchange of ideas and authoritative views by leading professionals which covers the entire research related to Bacteriology, Parasitology and beyond to confront the most challenging dilemmas in healthcare and uncover new solutions.
Why to attend:
Microbiology Conf 2023 Conference is a multidisciplinary program with broad participation with members from around the globe focused on learning about microbiology research and its advances. This is your best opportunity to reach the largest assemblage of participants from microbiology community that is from academia, microbiology entities, medical groups, labs, related associations, societies and also from government agencies, pharmaceutical, biomedical and medical device industries. This conference conduct presentations, distribute information, meet with current and potential scientists, make a splash with new clinical research developments, and receive name recognition at this Virtual event. World renowned speakers and the most recent techniques, developments, the newest updates in Molecular Microbiology are hallmarks of this conference.
Target Audience:
- Microbiology researchers
- Clinical researchers
- Pathologists
- Immunologists
- Researchers
- Scientists
- Pharmacists
- Biotechnologists
- Medical device industries
- Molecular biologists
- Genetic engineers
- Cellular microbiologists
- Environmental specialists
- Bacteriologists
- Virologists
- Veterinary microbiologists
- Computational biologists
- Hospitals, labs and association
- University Professors
- Research Scholars
- Laboratory technicians
- Students
Track 1: Clinical Microbiology and Biotechnology
Clinical Microbiology is a branch of clinical science that deals with the prevention, diagnosis, and study of disease transmission as well as the treatment of infectious diseases. It is concerned about a variety of clinical uses of microbes for health enhancement. Biotechnology is the use of biological processes for industrial and other uses, particularly the genetic manipulation of microbes for antibiotic and hormone synthesis. Biotechnology encompasses a wide range of topics such as biochemistry, genetics, microbiology, chemistry, and engineering.
- Virology
- Nematology
- Biotechnology in medicine
- Biotechnology in agriculture
- Biotechnology for industry
- Ropinirole
Track 2: Pharmaceutical Microbiology
Pharmaceutical microbiology is a branch of microbiology that is used in the pharmaceutical industry. It covers research into anti-toxins, chemicals, nutrition, antibodies, and other pharmaceutical products. It also incorporates the study of microorganisms that produce pharmaceutical contamination, as well as the debasement, disintegration, and deterioration of pharmaceutical crude. It is a branch of microbiology that recognises that nature's incredible diversity of microbes is rich with possibilities, some of which are useful and others of which are dangerous. The development of appropriate substrates for the manufacture of pharmaceuticals, food supplements, and mechanical solvents, as well as the development of the various antibodies that have been so important to the growth of global health, are all examples of useful areas.
Applications:
- Biotechnology
- Agriculture
- Medicine
- Food microbiology
- Bioremediation
Track 3: Discovery and Pharmacology of Antibiotics
Antibiotics are medications that are used to treat infections caused by bacteria. Bactericidal means that they can kill germs. They can also bacteriostatically impede their growth but not kill them. Antibacterial agents are often classified as one of four instruments, three of which are the inhibition or regulation of chemicals related to cell divider biosynthesis, nucleic acid corrosive digestion and fix, or protein blend, respectively. The disruption of layer structure is a part of the fourth system.
- Carbapenems
- Monobactams
- β-Lactamase inhibitors
- Aminoglycosides
- Tetracyclines
Track 4: Interaction and Side-effects of Antibiotics
Because antibiotics can interact with a variety of medications, it's critical to inform your primary care physician if you're taking any other prescriptions. Antibiotics, for example, may interact with blood thinners and acid neutralizers. A few antimicrobials have been shown to reduce the effectiveness of contraceptive pills. Anti-toxins are recommended by experts to cure bacterial illnesses. The majority of the side effects associated with anti-infection drugs are not dangerous. Antimicrobials, on the other hand, can occasionally induce significant reactions, such as hypersensitivity.
- Theophylline
- Probenecid
- Tizanidine
- Glibenclamide
Track 5: Applications of Microbes
Microorganisms are useful for distributing nutrients, treating waste water, producing biofuels, and producing a wide range of synthetic chemicals and proteins. They're used as biological systems in study. They've been weaponized and are occasionally used in combat and bioterrorism. They can be found in a variety of naturalistic environments, ranging from the dirt we use to grow our food to the stomach-related structures we use to process it. To survive and reproduce in any environment, organisms must be able to obtain nutrients, manage toxins, and deal with competitors and predators.
- Enzymes
- Production of steroid
- Organic acids
- Insecticides
Track 6: Environmental Microbiology
The study of the structure and physiology of microbial networks in the environment is known as environmental microbiology. The study of microorganisms in nature has been transformed by molecular biology, which has increased our understanding of the formation, phylogeny, and physiology of microbial networks. Microbiology, like the biotechnology industry, is an applied science that aids farming, health, and medicine, as well as environmental preservation. Microorganisms play an important role in our daily lives.
- Protozoology
- Mycology
- Nematology
- Physiology of microbes
- Ecology of microbes
Track 7: Genetic Engineering in Microbiology
Genetic engineering is the purposeful manipulation of DNA using laboratory processes to alter the characteristics of living organisms. Whether or not the species being altered are microbes, the substances and processes used are commonly adapted from microorganisms for use in increasingly complex organisms. Genetic engineering, also known as hereditary control or hereditary alteration, is the use of biotechnology to influence the characteristics of a living organism. It refers to a variety of technological developments that have been utilised to alter the genetic makeup of cells, including the exchange of traits within and across species boundaries in order to create better or novel living beings.
- Electrophoresis on a Gel
- Recombinant DNA
- Polymerase Chain Reaction
- Genetically modified organism
Track 8: Microbial Biofilms
Biofilms are a collection of microbial cells that are associated with plaque, pond scum, or foul buildup in sinks. Molding, connection, metabolism, and separation are all grouped together in this development. Biofilm development is a process in which microorganisms attach to and grow on a surface in an irreversible manner, producing extracellular polymers that promote connection and framework arrangement, resulting in a change in the phenotype of the living beings in terms of development rate and quality interpretation. Biofilms are created by a variety of microorganisms, including pathogens, and provide a means for these living creatures to protect themselves from antimicrobial agents.
- Dental plaque
- Bacillus
- Lactic acid bacteria
- Lactobacillus
Track 9: Bioremediation and Biodegradation
Biodegradation is the process of microorganisms breaking down natural materials in the environment. It's a naturally catalysed reduction in the complexity of concoction blends. To be clear, biodegradation is the process by which live microbiological living creatures break down natural compounds into smaller mixtures. Mineralization is the process that occurs when biodegradation is complete. Bioremediation is a waste management technique that uses natural operators to remove toxins from the environment. It addresses a natural problem, such as contaminated soil or groundwater. In an uncontaminated environment, bacterial growths, and other microorganisms are constantly grinding away at natural matter, separating it.
- Phytoremediation
- Mycoremediation
- Bioventing
- Bioleaching
- Bioreactor
Track 10: Recombinant DNA Technology
The recombination of DNA particles from two distinct species is known as recombinant DNA technology. It is implanted into a host living form in order to develop novel hereditary mixtures that are beneficial to science, medicine, agriculture, and industry. Individual DNA fragments from any genome can be introduced into vector DNA molecules like plasmids and amplified in bacteria independently. A DNA clone is a single amplified segment. Sickle-cell disease and Huntington's disease are among the hereditary illnesses for which DNA technology is being utilised to aid diagnosis.
- Sequencing of DNA
- Chain polymerase reaction
- Gel electrophoresis
- DNA cloning
Track 11: Bacteriology & Parasitology
Bacteriology is a discipline of science that studies the morphology, nature, genetics, and organic chemistry of microbes, as well as a variety of other aspects associated with them. The differentiating characteristics, organisation, and representation of bacterial species are all covered in this area of microbiology. It focuses on germs that cause disease in humans. The study of parasites, their hosts, and their interactions is known as parasitology Parasitologists look at parasites in all forms, including diseases, bacteria, and worms.
- Protozoa
- Helminths
- Ectoparasites
- Multicellular animal parasites
- Archaea
Track 12: Virology and Pathology
The study of viruses and infection-like entities, including their taxonomy, disease-causing qualities, development, and genetics, is referred to as virology. It is included in the field of microbiology. A virion is a single viral molecule that contains a variety of properties wrapped inside a protective protein shell called a capsid. The study of diseases is termed as pathology. It supports many aspects of patient care, from screening procedures and preventing disease. In pathology, doctors and researchers are experts in illness and disease.
- Anatomical pathology
- Clinical pathology
- Molecular pathology
- DNA viruses
- RNA viruses
- DNA-RNA viruses
Track 13: Infectious Diseases
Infectious diseases are illnesses brought on by organisms such as microscopic organisms, infections, growths, and parasites. Some infectious diseases can be spread from person to person via bodily emissions, creatures, or other means. SARS, the flu, the common cold, tuberculosis (TB), and hepatitis A and B are all used as models. Fever, diarrhoea, fatigue, muscle pain, and coughing are all symptoms of infectious infections.
- Malaria
- Hepatitis C
- Dengue
- Tuberculosis
- Cholera
Track 14: Genetic Syndromes & Gene Therapy
Gene therapy focuses on the defective genes that cause hereditary illnesses. Inheriting a defective (mutated) gene can result in a variety of diseases, including cystic fibrosis and haemophilia. It can also make you more susceptible to some malignancies. Gene therapy can be used to either replace a damaged gene with a healthy one or introduce a new gene that can cure or modify the consequences of a disorder.
- Hereditary illnesses
- Cystic fibrosis
- Gene therapy
- Haemophilia
- Gene
Track 15: Microbial Metabolism
Metabolism is the dynamic balance between catabolism and anabolism reactions that provide energy and building materials to the cell, as well as those that use them.
- Autotrophic
- Heterotrophic
- Mixotrophic
- Lithotrophic
- Organotrophic
Track 16: Vaccines & Antibiotics Production
Vaccines are preparations that contain generally deceased microorganisms such as bacteria or viruses and are administered via injection to increase protection against a specific disease. A vaccination is a method of increasing your body's natural immunity to a disease before you become ill. Antibiotics are made industrially by a fermentation method in which the source microbe is cultured in huge containers with a liquid growth medium. The antibiotic must next be removed and refined into a crystalline form once the process is complete.
- Toxoid vaccines
- Conjugate vaccines
- Penicillin
- Tetracycline
- Cephalosporin
Track 17: System Biology and Bioinformatics
The study of the interactions and behaviour of the components of biological entities, such as molecules, cells, organs, and organisms, is known as systems biology. Biological organisms are extremely complex, with various elements that interact in a variety of ways. The integration of computation and analysis tools to the capture and interpretation of biomedical data is characterized as bioinformatics. It is an interdisciplinary field that brings together computer science, mathematics, physics, and biology.
- Sequence Search Services
- Multiple Sequence Alignment
- Biological Sequence Analysis
Track 18: Enzyme Technology Advantages & Applications
Enzyme technology is being used in modern biotechnology for a variety of reasons, including the rapid manufacture of novel and practical goods. Chemical innovation entails altering a compound's structure or synergistic potential in order to produce new metabolites or participate in new response pathways. They are used in the preparation of foods and beverages, animal nutrition, materials, household cleaning, car fuel, and vitality ageing.
- Food production
- Washing powders
- Textile manufacture
- Leather industry
- Medical applications
Track 19: Coronavirus (COVID-19)
Coronaviruses (COVID-19) are a significant number of diseases that cause illness ranging from the common cold to more serious conditions such as Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Respiratory syndrome. Despite the fact that COVID-19 causes very minor symptoms in the majority of people, it can make a few people sick. Moreover, the condition can be fatal on rare occasions. The elderly, as well as those who have previously suffered from conditions such as hypertension, heart disease, or diabetes, appear to be becoming increasingly weak.
- Fever
- Cough
- Tiredness
- Loss of taste or smell
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
Track 20: Advanced Research in Microbiology and Public Health
The term "current research" refers to on-going study in the fields of basic and applied microbiology. Virology, mycology, bacteriology, parasitology, genomics, host immune responses, microbe characterization and evolution, virulence determinants, environmental microbiology, antibiotic resistance and production, drug and vaccine targets, prion diseases, cellular aspects of microbes, host pathogen relations, and many other disciplines were all investigated.
- Diagnostic microbiology
- Environmental microbiology
- Astro microbiology
- Agriculture microbiology
- Food microbiology
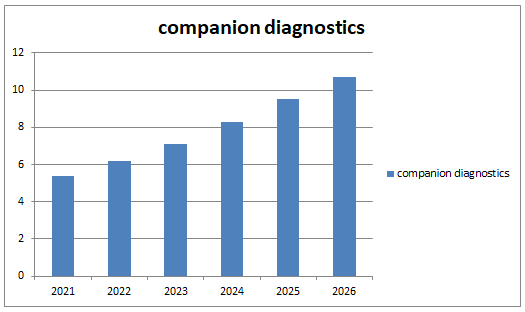
The global market for companion diagnostics (CDx) is estimated to grow from $5.4 billion in 2021 to reach $10.7 billion by 2026, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.6% during the forecast period of 2021-2026.
Companion Diagnostics: Global Markets provides a comprehensive analysis of the market in the global context, including market forecasts and sales through 2026. The report analyzes the market by segmenting it into the various product offerings: consumables (reagents, kits and panels), services and software. The segmentation also provides analysis by popular technology types such as PCR, next-generation sequencing, in situ hybridization (ISH), immunohistochemistry (IHC) and others.
This study surveys the companion diagnostics market by application into different therapeutic areas. The market is also assessed in three major geographic regions: North America, Europe and Asia-Pacific (APAC). The APAC markets include countries like India, China, Korea, Japan, Taiwan, Australia and New Zealand.
The industry structure chapter focuses on the changing market trends, market players and their leading products. This chapter also covers the mergers and acquisitions and any other collaborations or partnerships that happened during the evaluation period of this report that are expected to shape the industry.
Factors such as strengths, weaknesses, threats and opportunities that are expected to play a role in this market are evaluated in detail.
The scope of the report excludes the in vitro diagnostic products and their regulatory aspects. Also excluded are the nucleic acid-based tests in general, focusing solely on the companion diagnostics that meet the FDA definition.
3rd International Conference on Molecular Microbiology organized by Conference Series in Osaka, Japan during September 16-16, 2022 and was based on the Theme- Exploring Advanced Perspectives in Molecular Microbiology.
On behalf of our Organizing Committee, we would like to extend our appreciation for continued support and active participation of the Organizing Committee Member, Keynote Speakers and our Moderators for the successful completion of the Microbiology Conf 2022.
The Microbiology researchers and Clinical researchers, Immunologists, Computational biologists, Pathologists and Pharmacists, University Professors and Students from different countries actively participated in the Conference, discussed the most important trends and issues in Molecular Microbiology. Every Participant was having great reviews and had amazing experiences from the event.
Microbiology Conf 2022 was started by the opening ceremony which was followed by the Keynote speech and we are overwhelmed with their presence and generous response.
We would like to take the privilege to felicitate our keynote Speakers and honourable guests for their prominent contribution towards the smooth functioning of this esteemed event.
The eminent personalities at the conference were:
Dr. Huang Wei Ling | Medical Acupuncture and Pain Management Clinic | Brazil
Dr. Ryath Al-Hemedawi | Doctor of Clinical Microbiology | Iraq
Simom Silver | University of illinois | USA
Astghik Z Pepoyan | Nartional Agrarian University | Armenian
Ronald C. Montelaro | University of Pittsburgh | USA
In the last, we would also like to extend my ward regards to various delegate experts, Company representatives, eminent personalities who supported the Conference by facilitating active discussion forums. We would like to convey our sincere gratitude to all the supporters from Editorial Board Members of our Open Access Journals, Keynote Speakers, Honourable guests, Valuable Speakers, Students, delegates and special thank s to Media Partners for their promotions to make this event a successful one.
With the unique feedbacks from the Conference Microbiology Conf 2022, We would like to announce the commencement of the “4th International Conference on Molecular Microbiology” which is going to be held during August 17-18, 2023 Dublin, Ireland.
Let us meet again @ MICROBIOLOGY CONF 2023
Conference Highlights
- Clinical Microbiology and Biotechnology
- Pharmaceutical Microbiology
- Discovery and Pharmacology of Antibiotics
- Interaction and Side-effects of Antibiotics
- Applications of Microbes
- Environmental Microbiology
- Genetic Engineering in Microbiology
- Microbial Biofilms
- Bioremediation and Biodegradation
- Recombinant DNA Technology
- Bacteriology & Parasitology
- Virology and Pathology
- Infectious Diseases
- Genetic Syndromes & Gene Therapy
- Microbial Metabolism
- Vaccines & Antibiotics Production
- System Biology and Bioinformatics
- Enzyme Technology Advantages & Applications
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Advanced Research in Microbiology and Public Health
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | August 17-18, 2023 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Molecular and Genetic Medicine
- Journal of Genetic Syndromes & Gene Therapy
- Journal of Proteomics & Bioinformatics
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by